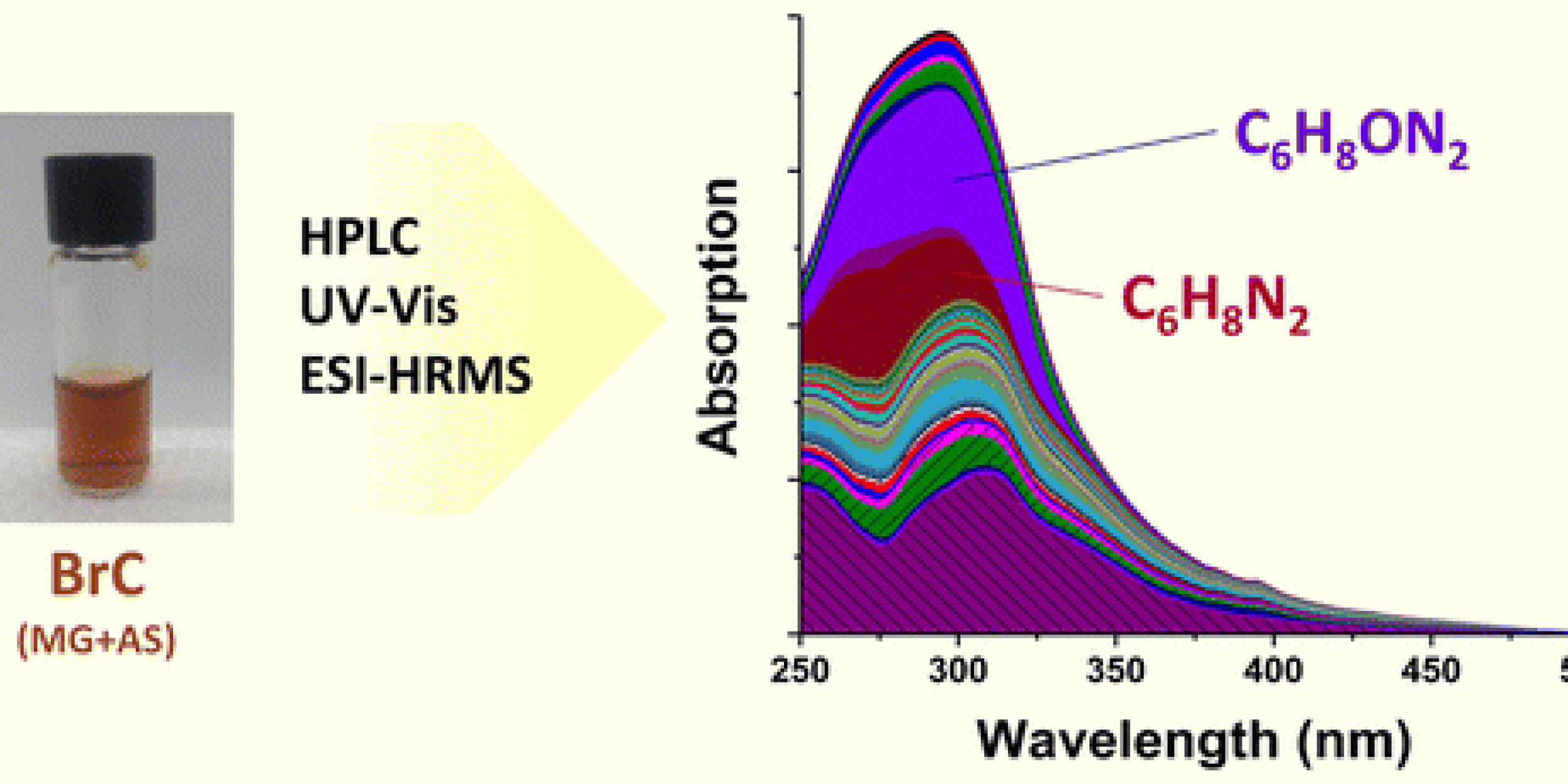
Research supported by CPO’s Atmospheric Chemistry, Carbon Cycle, and Climate (AC4) program was recently published in the Journal Environmental Science and Technology. The paper by Lin et al. focuses on the poorly-understood formation mechanisms of atmospheric brown carbon (BrC) chromophores.


Using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled to photodiode array detector and high resolution mass spectrometry, Lin et al.’s study investigates optical properties and chemical composition of individual BrC components produced through reactions of methylglyoxal and ammonium sulfate, both of which are abundant in the atmospheric environment.
Through this method, the researchers established a direct relationship between optical properties and chemical composition of 30 major BrC chromophores. Nearly all of these chromophores are nitrogen-containing compounds that account for more than 70 percent of the overall light absorption by the methylglyoxal and ammonium sulfate system in the 300−500 nm range.
According to the researchers, these results suggest that, “reduced-nitrogen organic compounds formed in reactions between atmospheric carbonyls and ammonia/amines are important BrC chromophores. It is also demonstrated that improved separation of BrC chromophores by HPLC will significantly advance understanding of BrC chemistry,” said the paper. This research was published on October 27, 2015.
To access a copy of the paper, visit: pubs.acs.org
Revealing Brown Carbon Chromophores Produced in Reactions of Methylglyoxal with Ammonium Sulfate