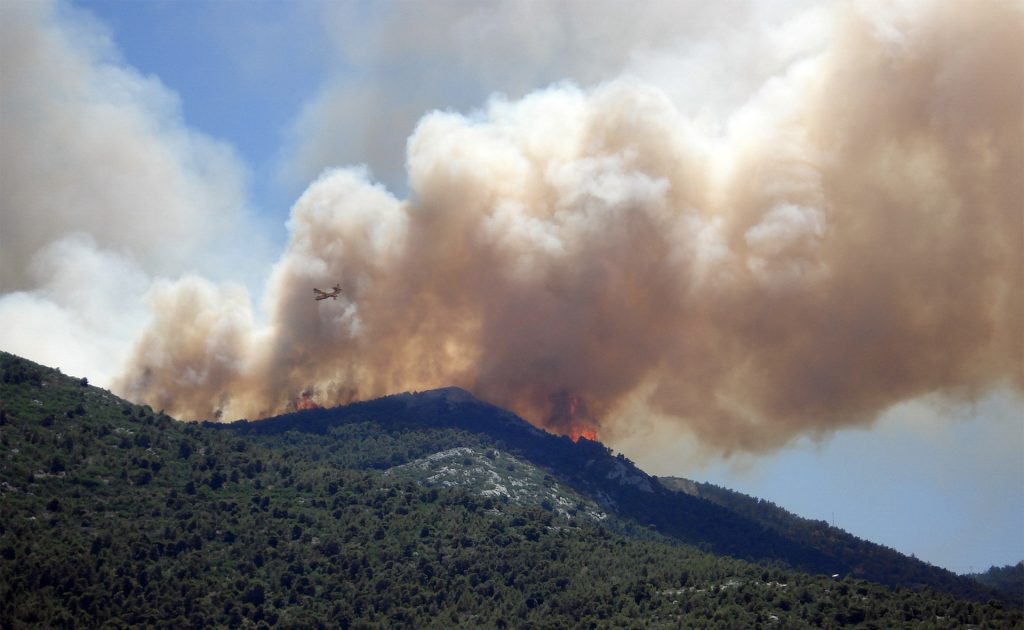
Using Aircraft Measurements to Investigate Primary vs. Secondary Sources of Organic Aerosols in Wildfire Plumes
This study, funded in part by Atmospheric Chemistry, Carbon Cycle, & Climate (AC4), investigates the relationship between primary and secondary sources of organic aerosols over the lifetime of a wildfire plume, finding at least half of the secondary sources are the result of evaporation of the primary sources.