Ocean heatwaves dramatically shift habitats
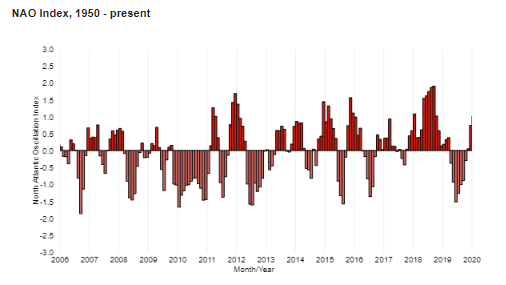
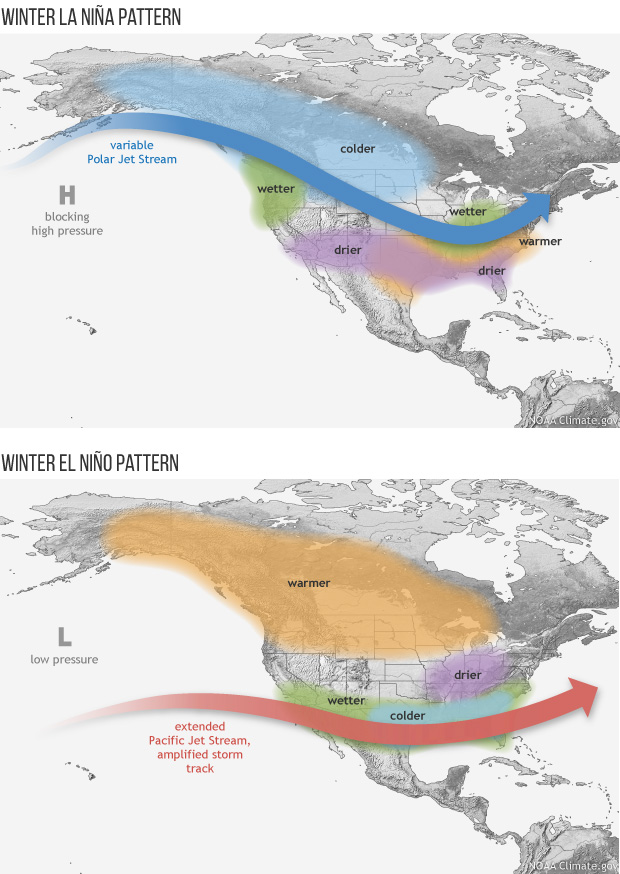
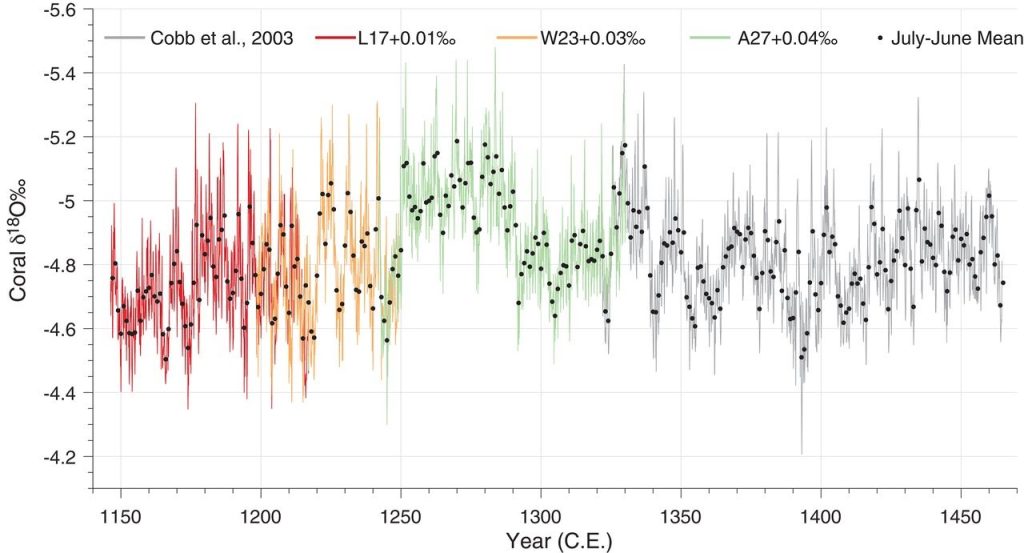
Marine heatwaves across the world’s oceans can displace habitat for sea turtles, whales, and other marine life by 10s to thousands of kilometers. They dramatically shift these animals’ preferred temperatures in a fraction of the time that climate change is expected to do the same, new research funded by NOAA’s Climate Program Office shows.
Ocean heatwaves dramatically shift habitats Read More »